This page is about the cylindrical reformulation by Robert Lipshitz. The main references are Lipshitz Paper, errata, and lecture notes in Heegaard Floer Homology.
Generic Pointed Heegaard Diagram and Intersection Points
Let be a pointed generic Heegaard Diagram.
Comment
The original two authors did not use the generic Heegaard diagram in the original formulation, but I guess we need this generic condition to evade the vacuously true in definition of admissible criterion.
Let denote ,and similarly define .
Domain
The curves divide into a collection of path-connected components as The closed sets are called the elementary domains.
A domain where is the algebraic multiplicity of the elementary domain .
Remark
We can also see the domain as a formal sum of the homology class in .
Multiplicity of a domain
The multiplicity of the domain at , denoted as , is the coefficient of the elementary domain containing in the expression for .
Intersection Point (Heegaard State)
An intersection point is a -tuple where ‘s lie on . In the book, authors defined as Heegaard State.
Remark
A structure depends on the choice of base point.
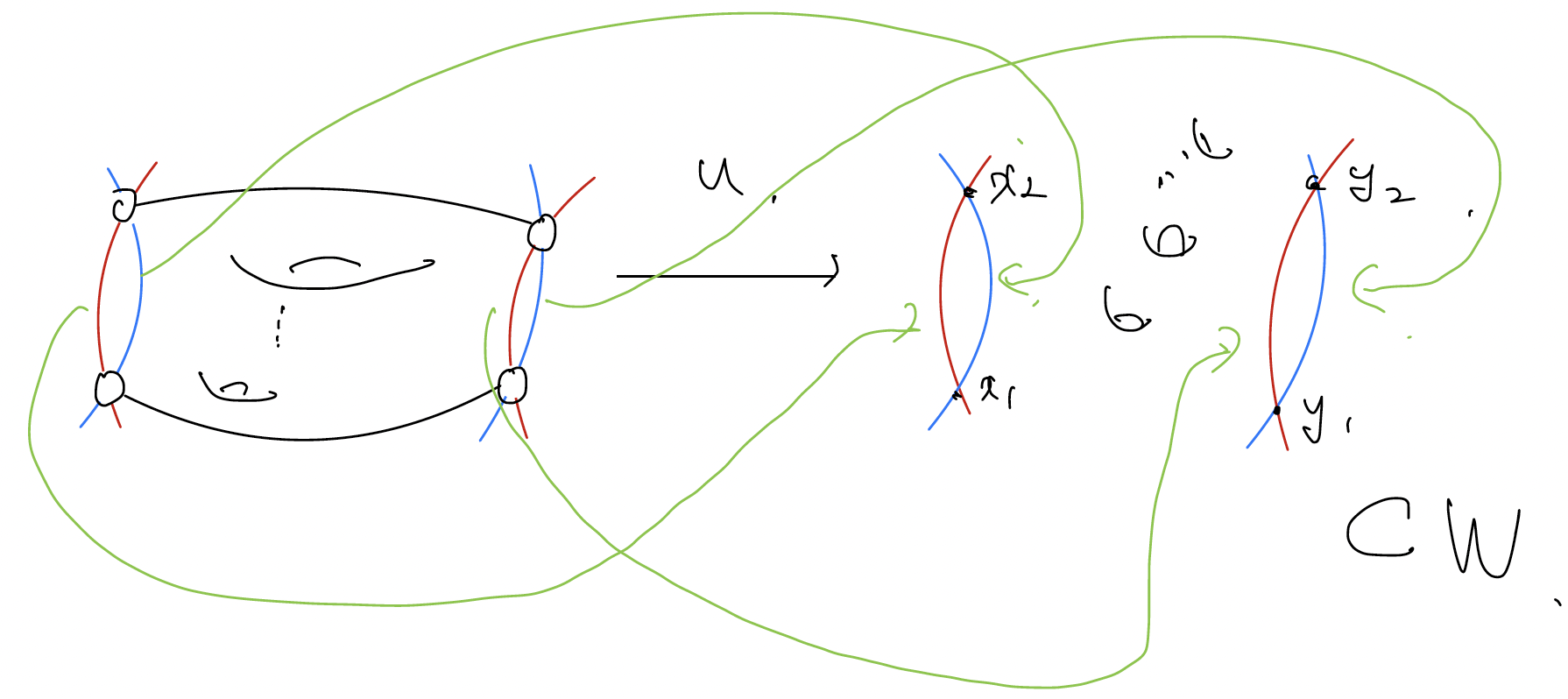
Cylindrical Construction
From now on I will assume and drop in as .
It is defined on by a technical issue.
Since we can stabilize the genus Heegaard diagram, the formulation can hold for the -manifolds.
Let , and denote .
The projection maps , , and are projection maps to the subscript component.
Also, let the Lagrangian cylinders and .
We are going to count the holomorphic representative which has boundaries in .
Complex Structure
Let the Heegaard surface have a complex structure and area form .
Let the split symplectic form on .
Let be an almost complex structure on as follows:
- is tamed with . It guarantees the compactness of the moduli space.
- in a neighborhood of points splits as .
- is translation invariant in the -factor.
- Cauchy-Riemann equation .
- preserves for all .
The conditions 3 and 4 make a cylindrical setting.
Characteristic Foliation
Through the symplectic form , for each , we have a characteristic foliation
Proof of it The kernel of restricted to , equivalently, it is the set of satisfiying for each . Since and is an area form that non-degenerate, . Therefore .
Let be an intersection point.
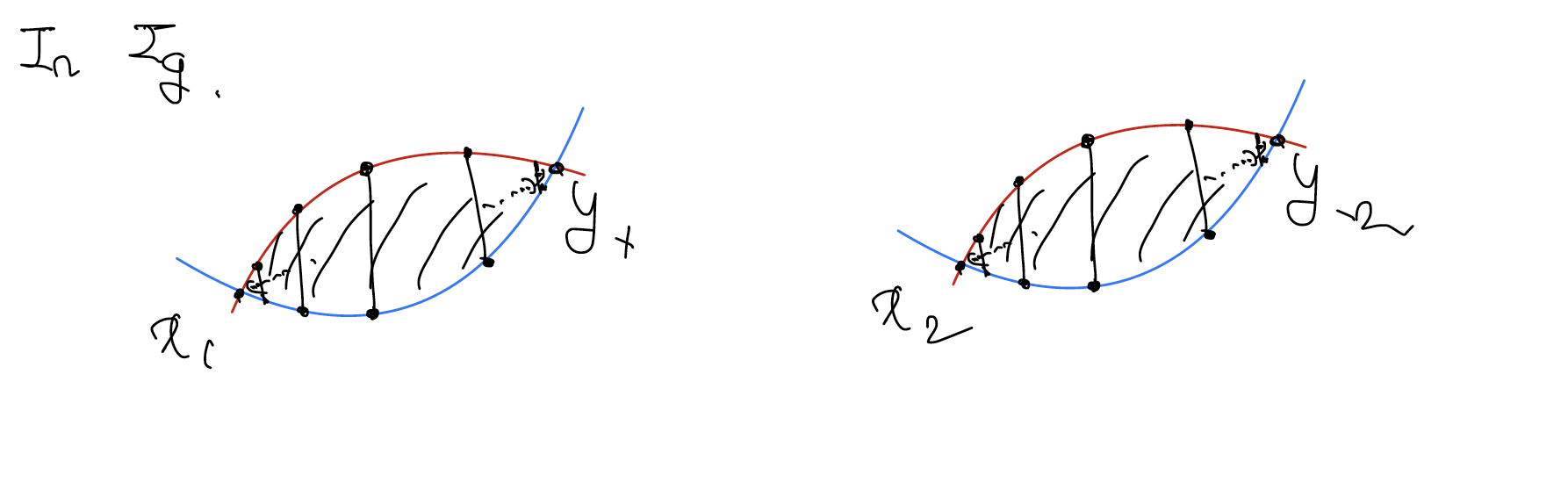
Since we have a characteristic foliation, we have Reeb chords .
I-chord collection
A -tuple of Reeb chords at specified by an intersection point is called an I-chord collection.
We can compactify as , and let and be the closures.
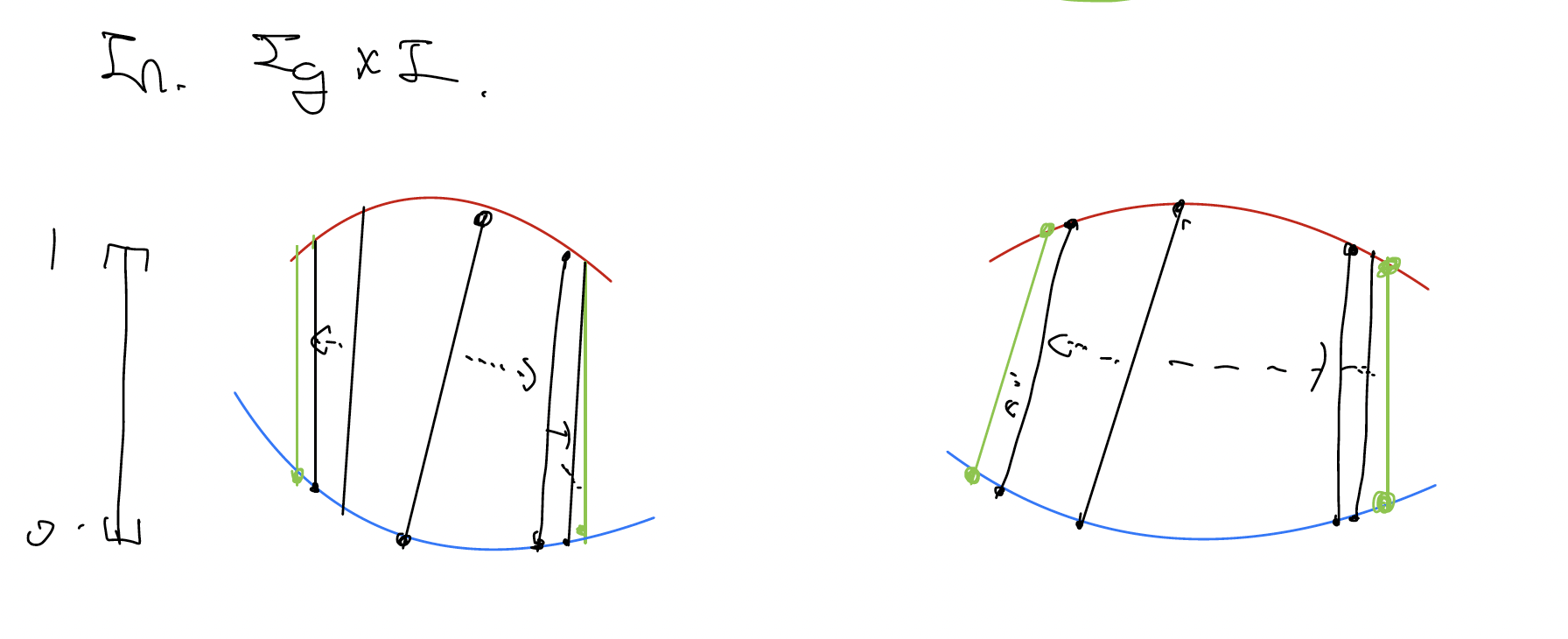
Holomorphic Curve and Connecting Domain
Let be a Riemann surface with boundary, with positive punctures and negative punctures .
does not need to be connected and is compact away from the boundaries.
Holomorphic Curve Conditions
Let be -holomorphic, satisfying:
- is smooth.
- is an embedding.
- .
- No component has constant .
- Energy of is finite.
- , .
- For each , and each consist of exactly one component of .
Comment
I am not sure about the terminology “shadow”. My first thought was projection , but professor pointed out holomorphicity of the projection map.
Connects between two I-chord collections
A holomorphic curve converges to an I-chord collection near and near .
Denote as the set of homology classes of connecting from to .
Two homology classes and are equivalent if they are the same in
Concatenation: If and , then .
Positive homology class
is positive if for all .
Hat Pi 2
.
Elements in are periodic classes.
Positivity of Domains
If has a holomorphic representative, then .
The contraposition is useful to define the boundary map.
Moduli Space of the Domain
Moduli Space
Let be a domain of homology class .
is the space of holomorphic curves connecting and in class .
In the cylindrical setting, , and its compactification.
Maslov Index Computation
The selling point of the paper, in my opinion, is “we can compute Maslov index combinatorially!“. Cylindrical Formulation for Heegaard Floer Homology. 1
Admissibility
We need to ensure that the sum in the differential runs over finitely many positive domains
.
Admissible Criterion in Heegaard Floer Homology
Chain Complex of Heegaard Floer Homology
Example Computation of hat version of Heegaard Floer Homology
Footnotes
-
In Lipshitz’s paper has gaps in the proof. So, please check the errata. ↩